Organizations are constantly seeking ways to gain a competitive edge by transforming data into actionable insights through analytics. However, achieving analytical success goes beyond just collecting large volumes of data and building dashboards. The key to turning data into meaningful and actionable insights across the organization lies in a frequently overlooked area – establishing a strong foundation of data governance. Have you ever considered the critical role data governance plays in breaking down data silos, enabling collaboration across domains, and empowering organizations to make informed decisions and drive innovation? Let’s explore. Data governance:
-
- Promotes a proactive operating model for data sharing: A data governance council establishes an organizational operating model that promotes collaboration and data sharing. It also defines industry-specific applicable standards (e.g., HIPAA, PCI DSS, FINRA) and translates regulatory policies like GDPR, CCPA, and SOX to ensure responsible data sharing with privacy and risk controls. The council monitors for adherence, conducts compliance audits, and resolves conflicts for a proactive and compliant approach to data sharing.
- Enables data democratization through federation. Federated data governance allows business units to manage their data while adhering to overall governance policies. This approach makes governed data easily accessible, encouraging users to tackle challenges, generate hypotheses, and drive innovation. Data democratization promotes data discovery, stewardship, and a data-driven culture, leading to new products/services and revenue streams.
- Establishes context through metadata management: Effective data governance involves creating data dictionaries and business glossaries. Data dictionaries provide metadata, detailing data attributes and relationships, while business glossaries offer business context, enhancing data literacy and enabling cross-domain collaboration, and insight-sharing.
- Secures enterprise data through access control. Data governance aligns access privileges with a RACI model, ensuring only authorized individuals have access to sensitive data. Encryption, masking, and automated access management processes minimize data breaches and unauthorized use. By implementing measures that clarify policies and enforce accountability, data governance safeguards enterprise data assets while striking a balance between openness and protection.
The benefits of data governance are enticing and evident. However, many organizations still struggle to implement it due to various factors, such as lack of a one-size-fits-all approach, organizational complexity, resistance to change, and insufficient resources allocated to this. Implementing data governance requires:
-
- Commitment and investment from senior leadership, as well as ongoing engagement from stakeholders across the organization.
- Establishing clear roles and responsibilities, defining policies and procedures, implementing data management practices, and fostering a culture of data stewardship.
- A shift in mindset, where data is recognized as a valuable asset that needs to be managed and governed effectively.
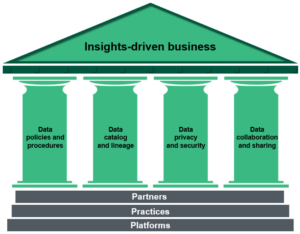
To address these challenges, organizations can turn to the four pillars of data governance that are supported by a strong foundation of partners, practices, and platforms enabling an insights-driven business (see Figure 1).
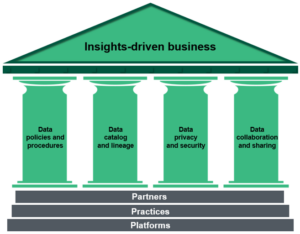
Figure 1: Pillars Of Data Governance Enable Insights-Driven Business
Implementing data governance holistically may involve significant effort and resources initially, but the benefits will increase exponentially over time. However, organizations must not wait to strive for perfection. Take the small steps immediately to meet where your organization maturity lies and evolve your data governance practice incrementally. Leverage the data governance capabilities already embedded in your existing data management solutions to build a strong foundation and evolve as your organization matures. As you show the value of data governance, you can seek investments to evolve into an advanced level of data governance maturity, achieve ambient data governance and incorporate new capabilities, roles, and practices. All these efforts will lead to greater benefits, including improved data quality, better data products, and a data-driven culture in the organization.
Would you like to know more about these four pillars with examples from real companies and how to invert the cost-benefit pyramid to gain increasing benefits from your governance program? Read the full report here. Want to connect with me? Schedule an inquiry or briefing.